Quick Start Guide¶
This guide walks through running KaryoScope clustering analysis on the Core-4 example dataset.
Prerequisites¶
- Python 3.11+
- Required packages: numpy, pandas, scipy, scikit-learn, matplotlib, pyranges
Installation¶
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/barthel-lab/KaryoScope-analysis.git
cd KaryoScope-analysis
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Example Data¶
The data/ directory contains feature-annotated telomeric reads from four cell lines:
| Sample | Group | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BJ | Primary | Primary fibroblast cell line |
| IMR90 | Primary | Primary fibroblast cell line |
| HeLa | Telomerase | Telomerase-positive cancer cell line |
| U2OS | ALT | Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres (ALT) cancer cell line |
Input files (data/raw_bed/):
- {sample}.telogator.1.KS_human_CHM13.subtelomeric.smoothed.features.bed.gz - Subtelomeric features
- {sample}.telogator.1.KS_human_CHM13.region.smoothed.features.bed.gz - Region features (satellites, arms)
Pipeline Overview¶
The analysis consists of two steps:
- Merge Feature Sets: Combine subtelomeric and region features using priority merge
- Run Clustering: Perform hierarchical clustering and enrichment analysis
Step 1: Merge Feature Sets¶
Merge subtelomeric and region features for each sample using --telomere-satellite-merge:
for sample in BJ HeLa IMR90 U2OS; do
python scripts/KaryoScope_merge_beds.py \
--bed data/raw_bed/${sample}.telogator.1.KS_human_CHM13.subtelomeric.smoothed.features.bed.gz \
data/raw_bed/${sample}.telogator.1.KS_human_CHM13.region.smoothed.features.bed.gz \
--output data/merged_bed/${sample}.telomere_region.merged.bed.gz \
--telomere-satellite-merge
done
What this does: - Takes telomeric features (canonical_telomere, noncanonical_telomere, TAR1, ITS) from the subtelomeric file as priority - Fills remaining positions with features from the region file (satellites, chromosome arms) - Outputs a single merged BED file per sample
Expected output:
=== Merging BJ ===
Subtelomeric intervals: 181,176
Satellite intervals: 1,212,339
Common reads: 2,681
Priority intervals: 106,893
Merged intervals: 1,301,492
Step 2: Create Sample Metadata¶
Create a sample metadata file (data/samples.tsv) that defines sample groups:
sample group color
BJ Primary #40D392
IMR90 Primary #60A5FA
HeLa Telomerase #F07167
U2OS ALT #FBBF24
Step 3: Run Clustering Analysis¶
Run the clustering analysis on merged BED files:
python scripts/KaryoScope_cluster_analysis.py \
--bed data/merged_bed/BJ.telomere_region.merged.bed.gz \
data/merged_bed/HeLa.telomere_region.merged.bed.gz \
data/merged_bed/IMR90.telomere_region.merged.bed.gz \
data/merged_bed/U2OS.telomere_region.merged.bed.gz \
--output-prefix results/Core4 \
--sample-metadata data/samples.tsv \
--comparison-mode per-sample \
--k-selection composite-knee \
--min-sequence-length 10000 \
--max-sequence-length 50000 \
--exclude-features "canonical_telomere*,novel,unknown" \
--umap \
--circular-dendrogram
Key parameters:
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
--comparison-mode |
per-sample |
Test each sample independently |
--k-selection |
composite-knee |
Auto-select optimal cluster count |
--min-sequence-length |
10000 |
Minimum read length (bp) |
--max-sequence-length |
50000 |
Maximum read length (bp) |
--exclude-features |
canonical_telomere*,novel,unknown |
Filter low-information features |
Expected runtime: ~5-6 minutes for 8,000 sequences
Output Files¶
The analysis produces the following outputs in results/:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
Core4.cluster_analysis.tsv |
Cluster statistics, enrichment p-values, sample composition |
Core4.sequence_assignments.tsv |
Per-sequence cluster assignments |
Core4.cluster_analysis.pdf |
Dendrogram and composition bar charts |
Core4.k_selection.pdf |
k-optimization diagnostics |
Core4.circular_dendrogram.pdf |
Circular dendrogram visualization |
Core4.umap.pdf |
UMAP projection colored by sample/cluster |
Core4.enrichment_bubble.pdf |
Enrichment significance bubble plot |
Core4.sample_percentage.pdf |
Sample composition heatmap |
Core4.log |
Full parameter log and runtime details |
Example Output Figures¶
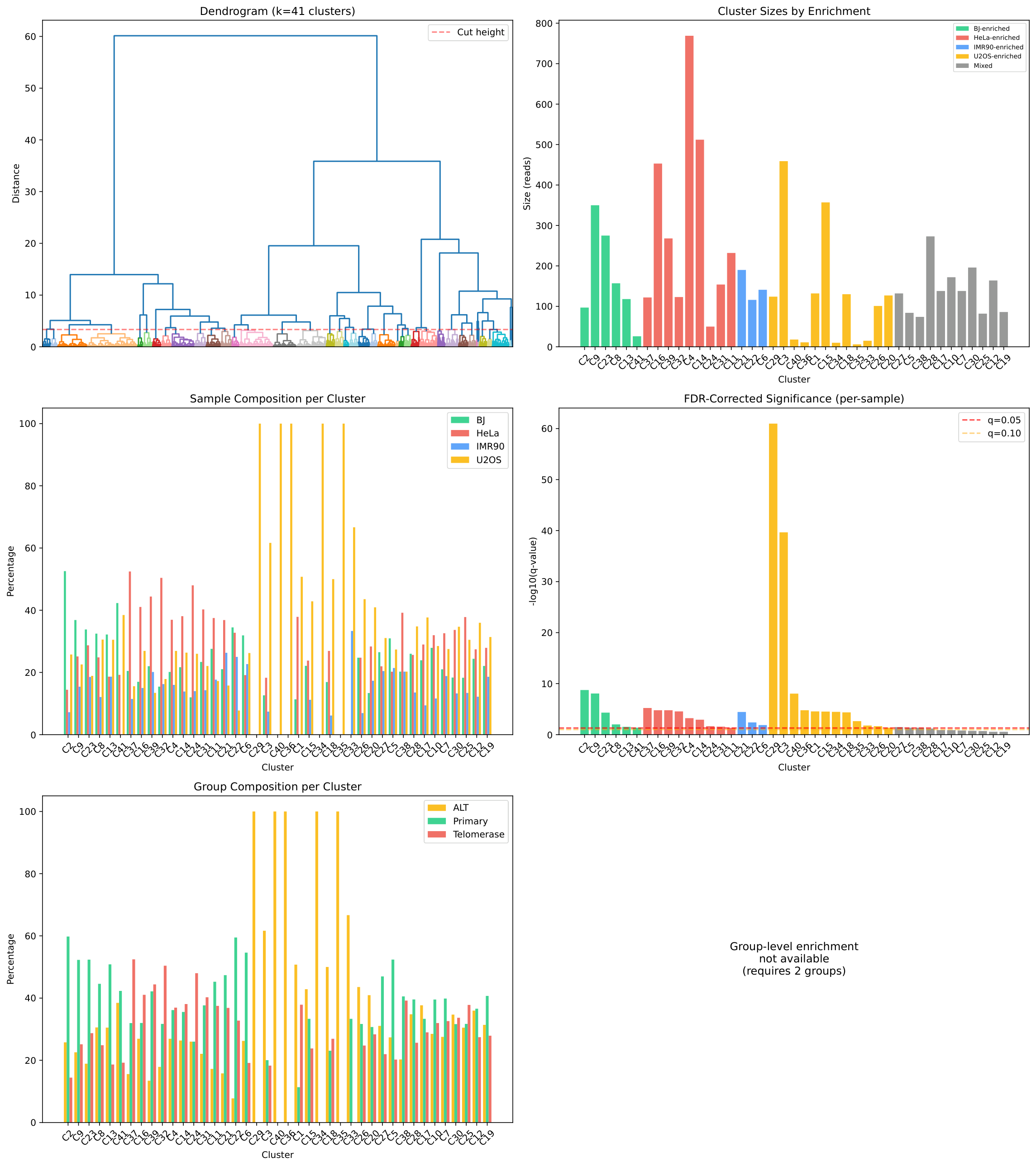
Cluster Analysis Overview¶
The main cluster analysis figure shows the dendrogram (left) and sample composition per cluster (right):
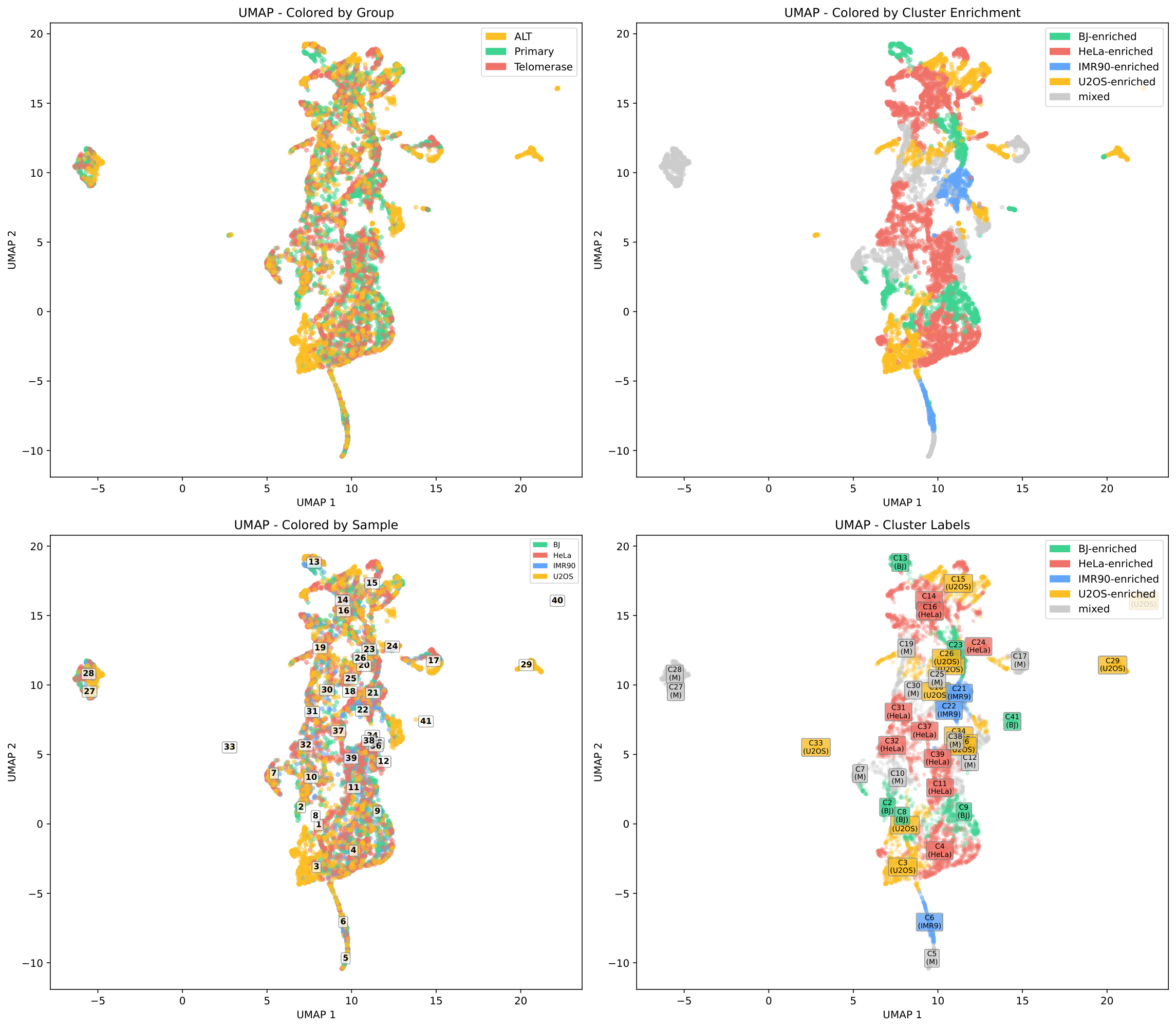
UMAP Projection¶
UMAP visualization shows sample separation in 2D space. Points are colored by sample (left) and cluster (right):
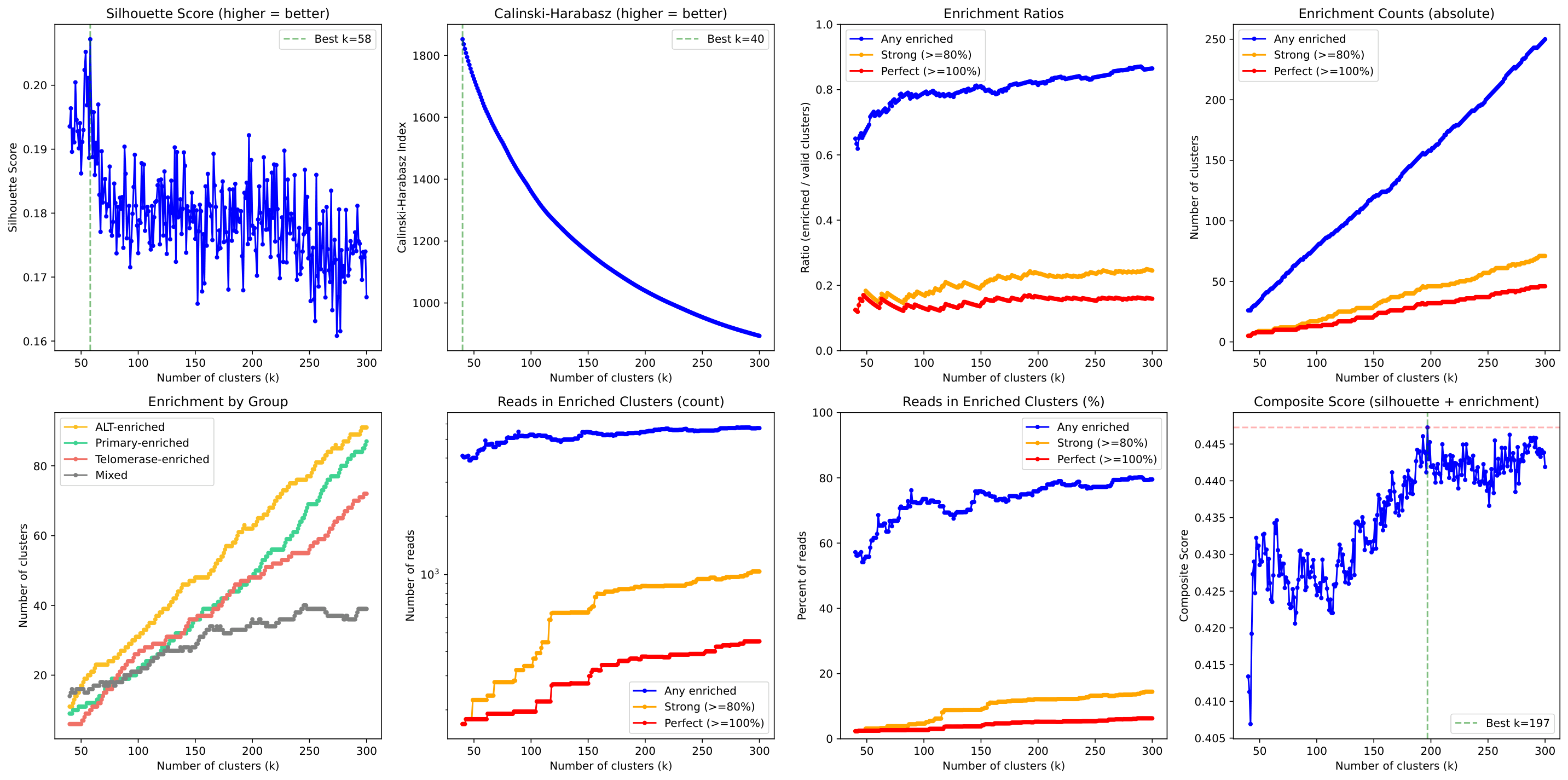
k-Selection Diagnostics¶
The k-selection plot shows how different metrics vary with cluster count, helping identify the optimal k:
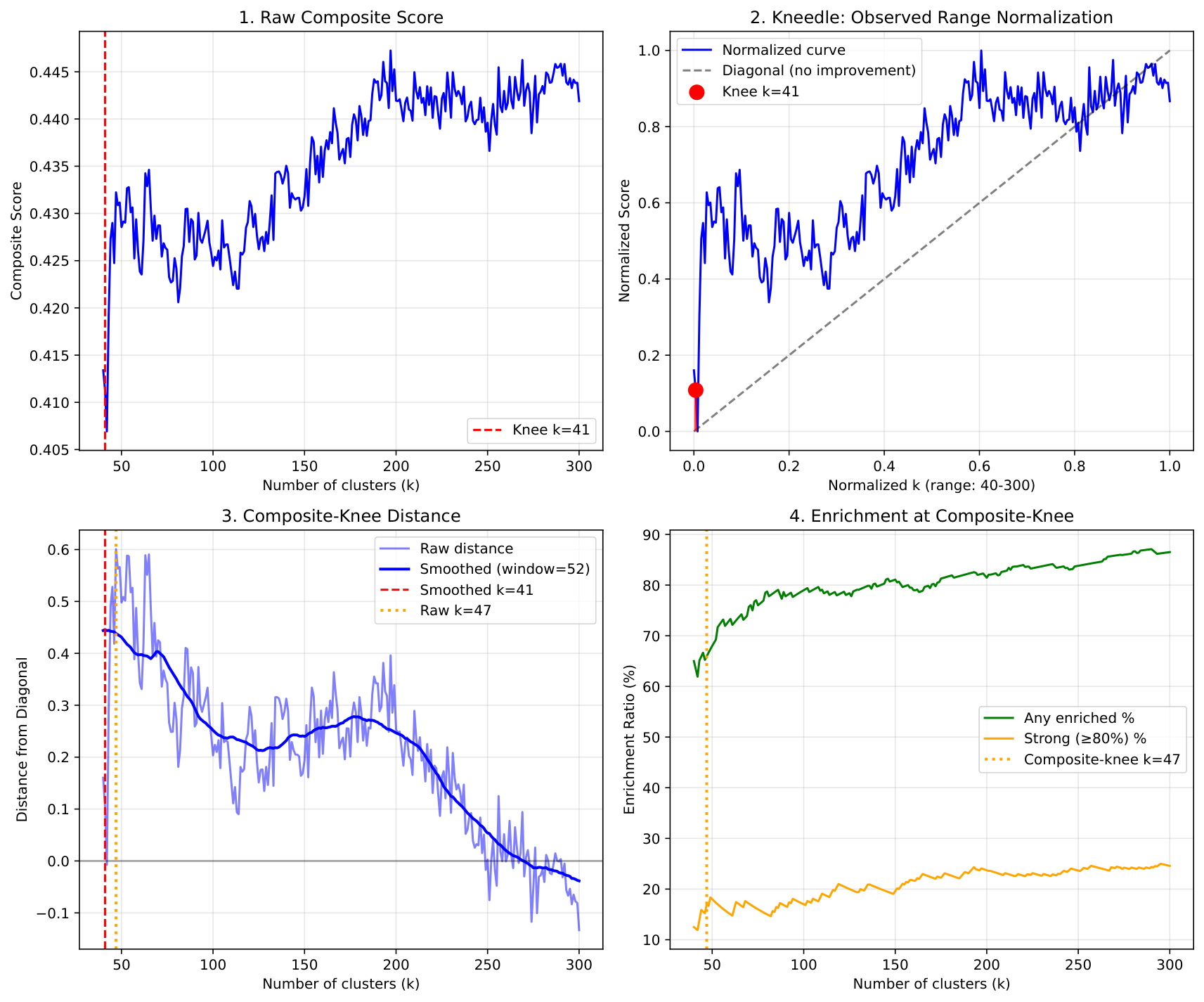
Composite-Knee Diagnostic¶
The composite-knee method finds the point of diminishing returns by measuring distance from the diagonal:
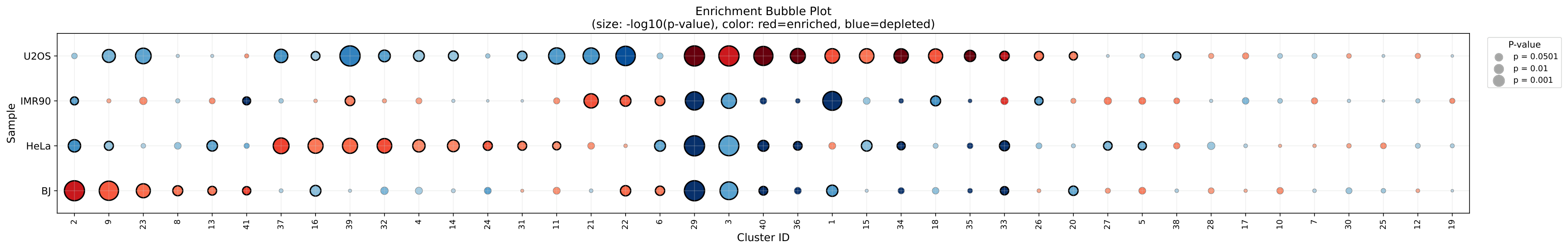
Enrichment Bubble Plot¶
Bubble size indicates cluster size, color indicates enrichment direction, and position shows statistical significance:
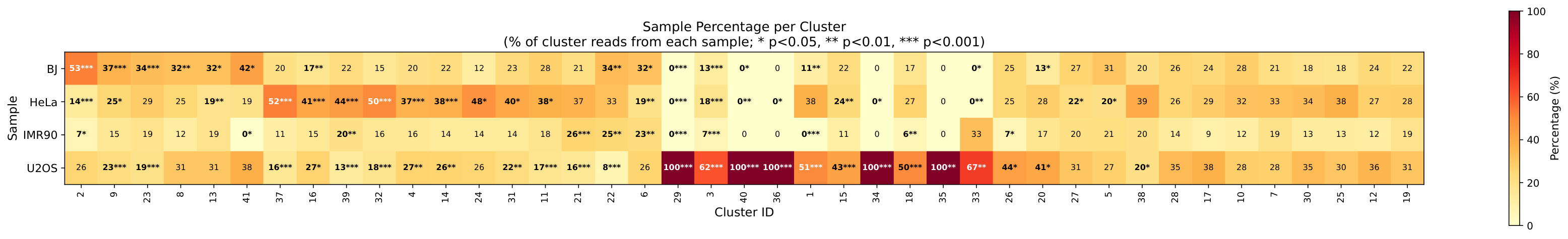
Sample Composition Heatmap¶
Heatmap showing the percentage of each sample within each cluster:
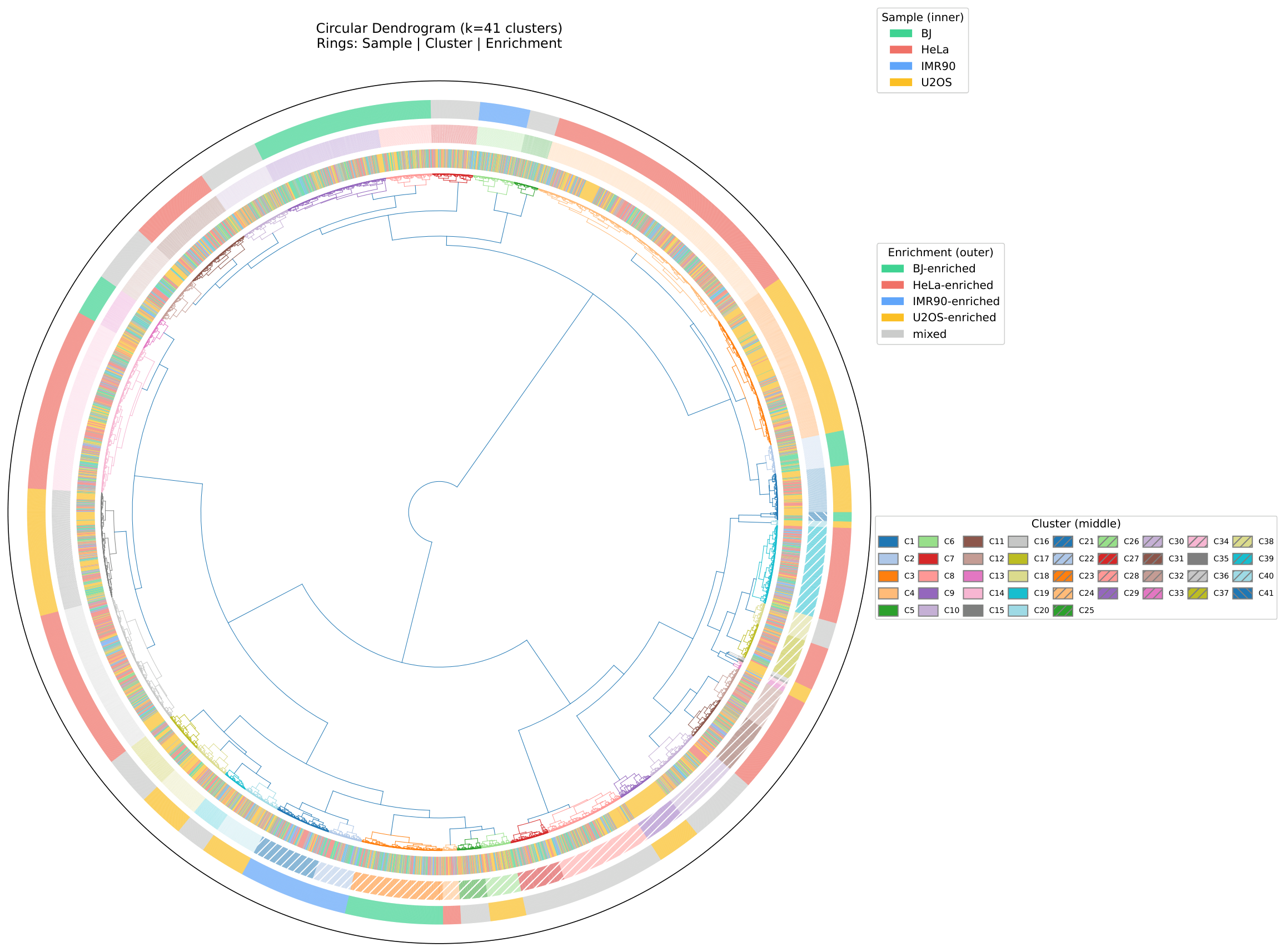
Circular Dendrogram¶
Circular dendrogram with sample annotations around the perimeter:
Interpreting Results¶
Cluster Summary¶
The analysis produces ~41 clusters with enrichment categories:
Summary
============================================================
Total sequences: 7,182
Number of clusters: 41
- BJ-enriched: 6
- HeLa-enriched: 9
- IMR90-enriched: 3
- U2OS-enriched: 12
- mixed: 11
Reading cluster_analysis.tsv¶
Key columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
Cluster |
Cluster ID |
Size |
Number of sequences in cluster |
{Sample}% |
Percentage of cluster from each sample |
P-value |
Fisher's exact test p-value |
Q-value |
FDR-corrected q-value |
Enrichment |
Enrichment call (e.g., "U2OS-enriched", "mixed") |
Centroid |
Sample of the centroid sequence (⚠️ = mismatch) |
Enrichment Categories¶
- Sample-enriched (q < 0.05): Cluster significantly over-represented by one sample
- mixed: No significant enrichment after FDR correction
Centroid Warnings¶
A ⚠️ next to the centroid indicates that the centroid sequence comes from a different sample than the enrichment label. This suggests cluster heterogeneity and may warrant further investigation.
Next Steps¶
- Visualize specific clusters: Use
KaryoScope_cluster_plot.pyto visualize reads from specific clusters - Explore the figures: Review the output PDFs for detailed visualization
- Check enrichment patterns: Look for sample-specific structural patterns in the enrichment results